Benefits of AWS Landing Zone
Organizations using AWS Cloud end up having several accounts for different purposes including the need to manage operations with separate accounts for different departments, deployments, new projects, functional requirements such as dev, test and production, etc. The reasons may be numerous but the underlying reason remains the same—operational efficiency which ironically is compromised as chaos and confusion grip the organization with budgets going haywire, utilization unmonitored and continuous struggle to enforce compliance.
To overcome these challenges AWS has designed Landing Zone which is an automated solution that enables users to launch and manage multiple accounts using AWS best practices. It is a solution wherein Amazon has brought together number of existing services to help customers manage accounts more efficiently. Using it, you can programmatically create multiple accounts through AWS Organization account and easily launch new template-based environments.
AWS Landing Zone brings the following benefits:
- You can create child accounts from AWS Organization with AWS Account Vending Machine. AVM leverages single sign-on to manage user account access in all accounts by which you can allow permissions and set restrictions to enforce policies and compliance.
- Landing Zones provides visibility into resource utilization across the organization, making it easy to ensure baseline security, and monitor and control IT budgets.
- Landing Zone is a great fit for organizations with multiple IT roles wherein you can control access to resources and restrict activities for different activities such as security, development, network and database administration, DevOps, etc.
- Landing Zone codifies AWS best practices such as CloudTrail and VPC; and DevOps practices such as infrastructure-as-code through CloudFormation templates and continuous delivery with CodePipeline.
Landing Zone Structure
Typically AWS Landing Zone solution includes four accounts: AWS Organization which deploys landing Zone and manages configuration and access; shared services account to host directory services; logging account usually stored in S3; security account to be used for audit and compliance purposes.
Architecture of AWS Landing Zone
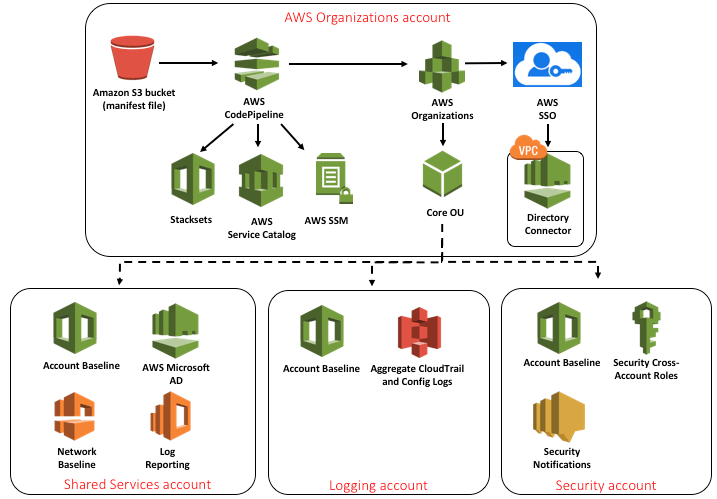
To implement Landing Zone, customers need to work with a professional service provider like Noventiq. We helped one of India’s largest players in mining implement AWS Landing Zone and achieve greater security and cost control by segregating accounts and creating a single pane for monitoring and controlling deployments.
Specific things we changed include:
- We created one account for shared services to host Active Directory and bastion host.
- Next, we isolated production environment as customer had several applications running dev, test and production from same account.
- A separate account was created to isolate external vendor who was developing one of the applications—enhancing security while ensuring only CloudFormation stack is used.
- Splitting up accounts for security helped monitor security posture of all accounts—monitoring compliance-related logging and auditing activities and storing security logs in a centralized bucket; sending alerts and taking corrective action during a breach.
- A distinct account for billing brought greater accountability facilitating analysis of usage, creating reports and sending alerts when billing thresholds are met.
Customer now has greater visibility across the organization resulting in better resource utilization, enhanced productivity and operational efficiency.
If you need help in streamlining your accounts, enhance transparency and manageability of deployments, contact us.







